The stock market is a dynamic and unpredictable environment where investors aim to grow their wealth over time. However, along this journey, they often face periods of losses or downturns. These periods of loss are measured and quantified using a crucial metric known as drawdown. In this article, we will explore the concept of drawdown in the stock market, its significance, how it is calculated, and how investors can use this metric to make informed investment decisions.
What Is Drawdown?
Drawdown is a fundamental metric in the world of finance, and it represents the peak-to-trough decline in the value of an investment or portfolio. It measures the loss an investor experiences from the highest point to the lowest point during a specific period. Drawdown is often expressed as a percentage and is used to assess the risk and volatility of an investment. Confused? See the below image.
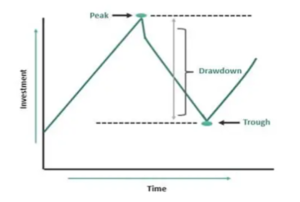
Drawdown consists of three key elements: the Peak, representing the highest point in a stock’s value over a specific timeframe. Trough, indicating the lowest point following the Peak; and Drawdown itself, which quantifies the loss as a percentage between the Peak and the Trough.
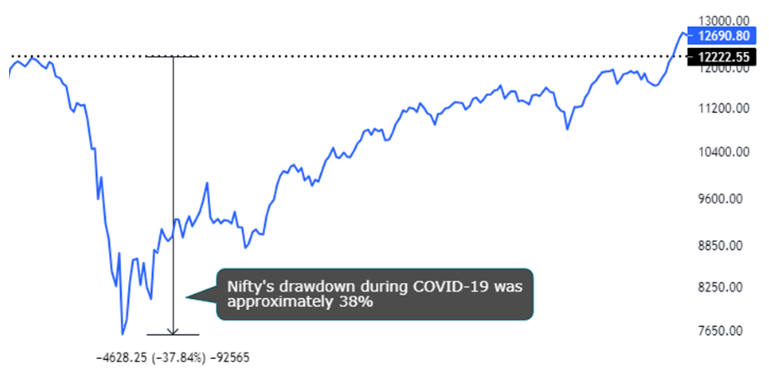
Nifty’s Drawdown During Covid-19
Why Drawdown Matters
Risk Assessment: Drawdown provides investors with a clear measure of the potential risk associated with an investment. A larger drawdown percentage indicates higher volatility and greater potential losses.
Psychological Impact: A drawdown can have a significant psychological impact on investors. Knowing how much their investment can potentially lose helps them manage their emotions and make rational decisions during market downturns.
Performance Evaluation: Investors and portfolio managers use drawdown to assess the historical performance of an investment or a portfolio. It allows them to evaluate the historical downside risk and make informed investment decisions.
Using Drawdown for Investment Strategy
- Risk Management: Investors can set predefined drawdown limits as part of their risk management strategy. For instance, if an investor decides to exit an investment when the drawdown reaches 20%, they can protect themselves from excessive losses.
- Asset Allocation: Drawdown can guide portfolio diversification. Investments with lower historical drawdowns may be favoured for capital preservation, while those with higher drawdowns may be preferred for potential growth.
- Historical Analysis: Studying the drawdown of an investment over time can help investors assess its overall stability and suitability for their financial goals.
In conclusion, we would like to mention that drawdown is a valuable metric for investors seeking to navigate the complex and often unpredictable world of the stock market. It enables them to assess potential risks, make informed decisions, and manage their emotions during periods of loss. By understanding drawdown, investors can better prepare to create a well-balanced investment strategy that aligns with their financial objectives and risk tolerance.


